The types of commonly used outdoor optical cables can be generally divided into two structures: central loose tube type and stranded type:
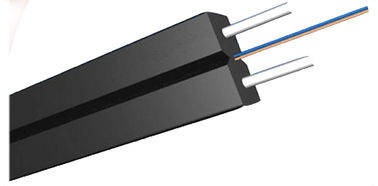
1.Central tube optical cable: The center of the optical cable is a loose tube, and the strength member is located around the loose tube. Such as the common GYXTW type optical cable, the number of cores of the optical cable is small, usually less than 12 cores.

Loose tube: The material of the loose tube is PBT, which is hard and flexible, and the side is compressive. Some factories will replace PBT with PP, and the cost can be reduced by half, but the optical fiber inside is easy to break during the transportation and construction of the optical cable. The color of PP is translucent.
Colored optical fiber: In order to distinguish each core optical fiber in the communication engineering of the optical cable, a layer of colored plastic is extruded on the bare fiber. The outdoor optical cable is to dye each core bare fiber with ink of different colors. The color of the ink is the same as that of the indoor cable, and there are also 12 types. The industry standard color spectrum of the Ministry of Information Industry is arranged as follows: blue, orange, green, brown, gray, nature( white), red, black, yellow, purple, pink, green. The use of natural colors instead of white is permitted provided that identification is not affected.
Color-locked optical fiber: In order to protect the optical fiber, a layer of 250 micron translucent resin is coated on the surface, and when the optical fiber is made into an optical cable, each core optical fiber needs to be colored with a different color. Some optical fiber manufacturers cover the optical fiber during production. It is a resin with 12 different colors, so that the optical fiber cable factory does not need to be colored again when it is used. The advantage of doing this is to save a coloring tool, but the disadvantage is that it cannot be used to flexibly distribute fibers.
Water-blocking tape: The water-blocking tape is made of water-blocking powder added between two layers of non-woven fabrics. Once the optical cable enters water, the powder will expand dozens of times after absorbing water, and a jelly-like gel will be formed to block the water and go deeper into the optical cable.
Non-woven fabric: Some manufacturers will replace the water-blocking tape with a non-woven fabric that is much cheaper than the water-blocking tape to reduce costs. There is no difference in appearance. Once the outer sheath of the optical cable is broken, the non-woven fabric cannot block water.
Corrugated steel strip: the outer surface of the water blocking strip is covered with a corrugated steel strip. The main function of the steel strip in the optical cable is to resist lateral pressure, tensile strength, mouse bite, and protect the bundle tube.
Steel wire: We can see two parallel steel wires on the outside of the steel belt. The function of the steel wire is to enhance the tension of the optical cable. The steel wire with a gray surface is phosphating, and the silver wire is galvanized to prevent the wire from rusting. Galvanized steel wire is more expensive than phosphating steel wire.
Optical cable sheath: Outdoor optical cables generally use medium-density polyethylene (MDPE), and some customers specify high-density polyethylene (HDPE). The cost of using high-density PE is slightly higher. There are also orders specifying that low-smoke and halogen-free materials (LSZH) should be used as sheaths. Many manufacturers also use recycled materials as optical cable sheaths to reduce costs. The optical cables made of this material have rough skins, contain a lot of impurities, and are prone to cracking and water seepage. The source of recycled materials is to crush some wire and cable skins, plastic bottles, slippers, etc. and return them to the furnace for re-granulation.
Because there are only 12 colors of optical fibers, the international standard central bundle tube optical cable can only have 12 cores at most. There are also some non-standard central beam tube cables with more than 12 cores, but generally no more than 24 cores. The method is to select one of the two optical fibers of the same color and spray a bar with an inkjet printer at a certain distance to distinguish them. Cables with more than 12 cores generally use layer twisting.
Small central loose tube fiber optic cable (JET)

This structure is widely used in the world. Glass fiber yarn (or aramid fiber, high-strength yarn) is added to the bundle tube with optical fiber and then the sheath is extruded. The optical cable is relatively soft, has a certain tensile force, and can be used indoors and outdoors. Aerial and easy to wear pipes.
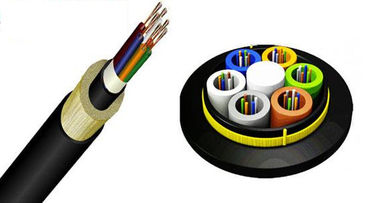
2.Layer stranded optical cable: multiple bundle tubes equipped with optical fibers are stranded on the central strength member in a twisted manner. Such optical cables such as GYTA, GYTS, etc., Through the combination of loose tubes, the optical cable with a large number of cores can be obtained. The color separation of stranded loose tubes usually adopts red and green color spectrum to separate colors, which is used to distinguish different loose tubes and different optical fibers. The number of cores of the layer twisted optical cable is relatively large, and it is produced with optical fiber ribbons, which can achieve more than a hundred cores.


Fiber optic cables with 60 cores and below often use a 5-tube structure, such as a 60-core fiber optic cable, with 5 bundle tubes, and 12 optical fibers in each bundle tube. Generally, for stranded optical cables below 12 cores, a bundle tube with 12 cores of optical fibers is used, and 4 solid filling ropes are twisted together. It can also be twisted with 2 6-core bundle tubes and 3 filling ropes, or it can be matched in other ways.
GYTS type optical cable: In the layer twisted optical cable, this type and GYTA are the most common. Twist several bundle tubes on a thicker phosphating steel wire, fill the gaps of the twisted cable with water-blocking cable paste, and wrap a circle of plastic-coated steel tape on the outside, and then extrude the sheath.
GYTA-type optical cable: This optical cable has the same structure as GYTS, except that the steel tape is replaced by aluminum tape. The lateral pressure resistance index of the aluminum strip is not as high as that of the steel strip, but the anti-rust and moisture-proof performance of the aluminum strip is better than that of the steel strip. In some environments where the pipe is worn, the GYTA type is used, and the service life of the optical cable is longer.
GYFTY-type optical cable: This type of optical cable is to twist several bundle tubes on a non-metallic reinforced core, fill the twisted gap with cable paste or keep a circle of water-blocking tape, and directly squeeze the sheath without adding armor.

There are many evolutions of this model. It is used in some overhead environments. In order to increase the tensile force of the optical cable, some aramid fibers should be added to the stranded cable core and then extruded sheath. If the central reinforcement uses steel wire instead of non-metallic reinforced core (FRP), the model is GYTY, without F (representing non-metallic)
FRP reinforced core: This material is generally made of glass fiber, and the strength of the same outer diameter is greater than the tensile force of the steel wire. It is characterized by non-conductivity, and it is safer to use overhead in a minefield environment. The optical fiber is drawn from high-purity glass, so it is not afraid of lightning, but the metal parts in the middle of the optical cable are easily damaged by direct lightning strikes when the optical cable is overhead. Seeing the model with F, we should know that it is mainly lightning protection. The cost of strengthening with FRP is slightly higher than that of steel wire.
Type 53 optical cable: We have seen some models such as GYTA53 and GYTY53. This type is a layer of steel armor and sheath on the outside of GYTA and GYTY optical cables. Applied in those occasions where the environment is relatively harsh. When you see 53, you should know that it is an extra layer of armor and an extra layer of sheath.
Physical drawing and section drawing of GYTA53 model

8-shaped optical cable: This type of optical cable is suitable for places with sparsely populated areas. A sling is added outside the bundled tube or layered optical cable. The sling is generally twisted with 7 steel wires with a diameter of 1.0 mm, or a A galvanized steel wire with a diameter of 2.5 mm.


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!